How to Measure Density: A Practical Guide for 2025
Understanding how to measure density is vital across various fields, including physics, engineering, and chemistry. With advancements in technology and methods, this comprehensive guide will delve into essential density measurement techniques to ensure precision in your experiments and applications. This guide will benefit students, professionals, and anyone interested in the intricate world of density measurement.
The Concept of Density in Physics
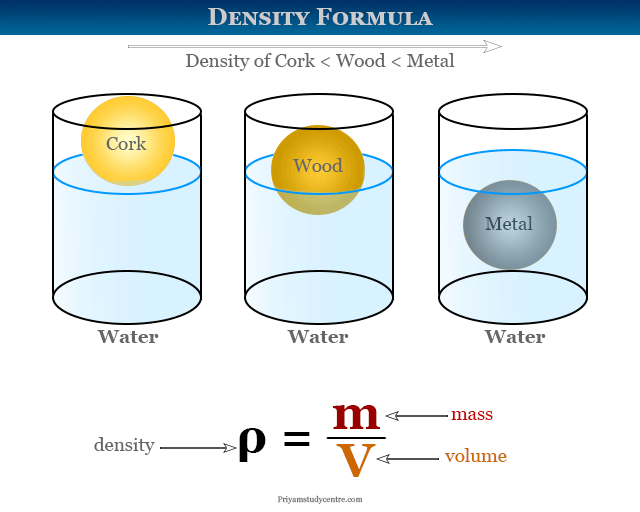
At its core, the concept of density refers to the mass of an object divided by its volume. This fundamental relationship is pivotal in understanding other physical principles, including buoyancy and pressure. Density can be defined using the density formula, which is expressed as: Density = Mass/Volume. The unit of density commonly used is grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) for solids and liquids or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) for gases. Understanding these units is crucial for accurate density determination in experiments.
Importance of Density in Science
Density has significant implications in various scientific fields. In density in chemistry, for instance, it helps determine the concentration of solutions. Similarly, density measurements in science are pivotal in identifying properties of materials. Hardened substances have a higher density compared to softer ones, and this variance aids in identifying material characteristics, thus making it an essential part of materials science. Moreover, understanding how density interacts with factors like temperature and pressure can lead to more accurate experimental outcomes.
Relation between Density and Buoyancy
The principles of density and buoyancy are directly tied. Archimedes’ principle states that an object submerged in a fluid experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced. This principle helps explain why some objects float while others sink. For instance, a ship is designed to displace enough water to support its weight despite having a high density of solids, showcasing the delicate balance between density and buoyancy.
Density Measurement Techniques
Precision in density measurement methods is crucial in various applications from laboratory tests to industrial processes. Several techniques can be utilized depending on the material type being analyzed, whether it is a density of liquids or solids, and the required precision.
Using a Hydrometer for Liquid Density
The hydrometer is a common device used for measuring the density of liquids. It consists of a calibrated glass tube with a scale on it. By floating the hydrometer in the liquid, one can determine the liquid’s density based on the level to which it sinks. This method relies on the hydrostatic pressure principle and is useful for determining specific gravity quickly. It is essential to ensure that the temperature of the liquid aligns with standard conditions for accurate readings.
Density Measurement Through Volume Displacement
The volume displacement method is another practical technique for measuring density, particularly for solids. In this method, an object is submerged in water, and the volume of water displaced is measured. By knowing both the mass of the solid (using a balance) and the volume it displaces, the density can be calculated easily. This method aligns closely with principles of fluid dynamics and is straightforward for solid materials that are denser than water but might require modification for lighter materials to avoid buoyancy errors.
Applications of Density in Industry
The applications of density in different industries are vast, emphasizing its importance in daily operations and research. Across the manufacturing sector, understanding density measurement is critical in quality control processes. False density estimations can lead to defects and product failures.
Density Measurement in Construction
In construction, density measurement in construction materials is crucial for ensuring structural integrity. For instance, knowing the density of concrete is important for load calculations and durability assessments. Utilizing standardized density values allows engineers to predict how a material will behave under stress. Ensuring that the correct density is achieved can prevent structural failures.
Density in Fluid Dynamics
Fluid density is a significant factor in fields involving fluid dynamics, such as aerodynamics and hydrodynamics. Accurate density calculations help in designing aircraft and submarines, where performance relies heavily on the properties of the fluids they traverse. Factors like temperature and pressure variations in fluids add layers of complexity, and precise density measurement devices become crucial in applications ranging from weather prediction models to hydraulic systems.
Challenges in Measuring Density
Despite advancements, measuring density can present several challenges. Differences in environmental conditions, such as temperature fluctuations, can significantly affect density calculations, particularly in fluids. Therefore, understanding how these external factors influence density is critical for researchers.
Variability Due to Temperature
The effects of density and temperature are particularly pronounced in liquids and gases. For example, as temperatures rise, both the mass and volume can change, leading to variances in density readings. It’s essential to conduct measurements at a standardized temperature to ensure accuracy.
Precision in Density Measurement
Ensuring precision in density measurement is vital, especially in sensitive applications like pharmaceuticals or food production. Instruments such as advanced digital densitometers help automate density readings, significantly mitigating human error. Regular calibration of these devices is also necessary to maintain accuracy in results.
Key Takeaways
- The concept of density is pivotal in understanding various physical laws.
- Different density measurement techniques are employed based on the state of the material (solid or liquid).
- Understanding the impacts of temperature and external factors is crucial for accurate measurements.
- Precise density readings are essential across multiple industries, influencing quality and safety.
FAQ
1. What tools are used for measuring density in liquids?
Common tools include hydrometers and digital densitometers. Hydrometers give a quick indication based on floating capabilities, while densitometers provide precise measurements by evaluating mass and volume more systematically.
2. How can temperature affect density readings?
Temperature changes can alter the mass and volume of liquids and gases, affecting density. Typically, as temperature increases, density decreases because substances expand. This relationship must be considered during calculations for accuracy.
3. What is the importance of specific gravity?
Specific gravity is a dimensionless quantity that compares the density of a substance to that of water. It plays a critical role in various applications, such as identifying materials and assessing their purity, particularly in laboratory environments.
4. How is density related to buoyancy?
Density influences buoyancy through Archimedes’ principle, stating that an object submerged in fluid experiences a buoyant force proportional to the fluid’s density. This principle explains why some objects float and others sink.
5. Can density measurement techniques be automated?
Yes, many modern laboratories utilize automated density measurement methods to improve accuracy and efficiency. These systems use digital sensors to reduce human error and allow for real-time tracking.