How to Effectively Find the Side of a Triangle
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various strategies and techniques to understand the **triangle side length**, calculate unknown values, and utilize formulas critical for solving triangle problems. Whether you are a student or a professional in technical fields, mastering the **triangle side rules** and properties is essential in geometry.
Understanding Triangle Properties
To find the **side of a triangle**, it is important to first grasp the fundamental properties of triangles. A triangle is defined by three sides and three angles. The relationship between these sides and angles forms the cornerstone of triangle geometry. Each triangle falls into specific categories: scalene, isosceles, and equilateral triangles, each having distinctive properties regarding their sides and angles.
Types of Triangles and Their Side Relationships
Triangles can be classified by their side lengths. An **equilateral triangle** has all sides and angles equal, which dramatically simplifies calculations regarding side lengths. In contrast, an **isosceles triangle** has two sides of equal length, allowing one to use these equal sides to find the third using basic algebra. Scalene triangles have all sides of different lengths, adding complexity to determining each **triangle side length** since each is unique.
Applying The Triangle Inequality Theorem
The **triangle inequality theorem** postulates that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the remaining side. This fundamental rule assists greatly in problems where you know two sides and need to deduce the length of the third. For example, if you have sides measuring 3 cm and 4 cm, the third side must be less than 7 cm (3+4) and greater than 1 cm (4-3).
Finding Unknown Triangle Sides Using Formulas
When working with triangles, several formulas can help you find an unknown side length. The **Pythagorean theorem**, applicable to right triangles, states that the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides equals the square of the hypotenuse. This relationship is vital when finding the hypotenuse of a right triangle. Moreover, the **law of sines** and the **law of cosines** provide powerful tools for solving for angles and side lengths in non-right triangles.
Methods of Calculating Triangle Side Lengths
There are numerous methods employed to **calculate triangle side lengths**, and selecting an appropriate method is imperative based on the given information. These methods may include direct measurement, geometric construction, or the use of trigonometric ratios.
Using the Law of Cosines
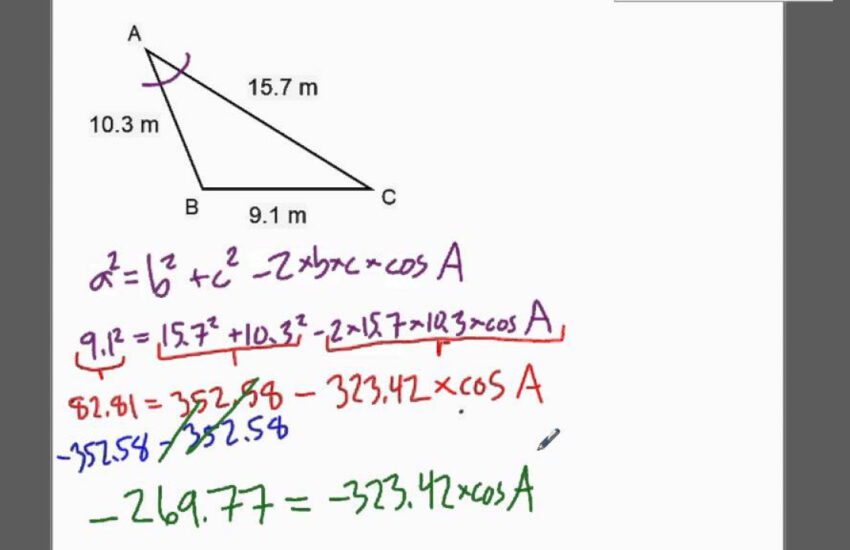
The **law of cosines** allows for the calculation of an unknown side when you know two sides and the included angle. The formula is c² = a² + b² – 2ab * cos(θ), where c is the side opposite the angle θ. This powerful equation not only provides the geometric relationship but also integrates angle measurements, confirming it as a staple in triangle side calculations.
Applying the Law of Sines
The **law of sines** is crucial when you’re given a triangle defined by two angles and a side (ASA) or two sides and an angle (SSA). The relationship sin(A)/a = sin(B)/b = sin(C)/c allows for resolution of unknown sides when compensating for other sides’ lengths and their opposite angle measures.
Interactive Triangle Calculators and Tools
In today’s technology-driven world, various online tools allow users to solve for triangle sides effectively. These **interactive triangle calculators** let you input known values and receive results for unknown side lengths across various triangle types. Using these interactive platforms enhances learning and provides immediate solutions for practical problems related to triangles.
Practical Applications of Triangle Measurements
The practical applications of triangle measurement are far-reaching, encompassing various fields such as architecture, engineering, and physics. Understanding how to find the **length of a triangle side** aids in the design and construction processes, ensuring structural integrity and functionality.
Using Triangles in Architecture
Triangles play a pivotal role in architectural design due to their inherent strength. By utilizing **triangle side proportions** in building structures, engineers can ensure durability and stability. Understanding how to calculate dimensions, including the **area of triangle** interplays effectively for maximal space efficiency within design layouts.
Triangle Applications in Physics
In physics, triangles help describe various physical phenomena using vector analysis. Concepts like **finding angles in a triangle** relate closely to resolving forces; thus, mastering the **congruency of triangle sides** is essential. You often encounter these applications in more advanced studies, such as determining equilibrium in structures or analyzing projectile motion.
Using Triangles in Navigation
Triangles also find their usage in navigation processes. By establishing a point of reference and measuring distances through **trigonometric ratios**, navigators can calculate positions and create accurate maps. Understanding how to compute corners and side proportions significantly aids in exploring new territories and entirely different landscapes.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding basic triangle properties is crucial for solving side length problems.
- The law of cosines and the law of sines are indispensable for finding unknown triangle sides.
- Interactive tools are invaluable for quick calculations and deeper understanding.
- Triangles are fundamental in practical applications across various disciplines.
- Mastering triangle side relationships can elevate problem-solving capabilities in mathematics and science.
FAQ
1. What is the formula to calculate the side of a triangle given two sides and an included angle?
The formula to use is the **law of cosines**: c² = a² + b² – 2ab * cos(θ). Here, a and b are the known sides, θ is the included angle, and c is the side being calculated.
2. How can I find the unknown side of a right triangle?
To find the unknown side of a right triangle, you can employ the **Pythagorean theorem**: a² + b² = c², where c is the length of the hypotenuse. This theorem applies only when dealing with right triangles.
3. What are the triangle types’ properties that affect side lengths?
Each triangle type has distinct properties affecting side lengths: equilateral triangles have equal sides, isosceles triangles have two equal sides, and scalene triangles have all sides unequal. Understanding these attributes is crucial for accurate calculations.
4. Can I use the triangle length to find the area?
Yes, you can find the area of a triangle if you know the base and height using the formula: Area = (base x height) / 2. The relationships between sides and angles facilitate this calculation effectively.
5. What is the significance of the triangle inequality theorem?
The **triangle inequality theorem** states that the sum of any two sides must be greater than the length of the third. This principle serves as a foundational rule for understanding triangle side relationships.
6. How can the law of sines help solve problems with triangles?
The law of sines is beneficial when addressing triangles with known angles and sides. This rule helps calculate unknown sides or angles based on the relationships established between known measures.
7. Is there an interactive way to learn about triangle sides?
Absolutely! Utilizing **interactive triangle solvers** allows learners to enter known measurements and see solutions for unknown sides, enhancing engagement and understanding in triangle theory.