How Many High School Credits Do You Need to Graduate in 2025?
As students and parents prepare for the upcoming school years, understanding the high school graduation requirements is crucial. This article explores the number of credits needed to graduate in 2025, focusing on the essential standards, credits breakdown for diploma, and more. Ensuring students meet the high school credit requirements is a fundamental step towards achieving a successful graduation. Let’s delve into the specifics.
Understanding High School Credit Requirements
Students often wonder, “What is a high school credit?” In simplest terms, a high school credit represents the completion of a course or subject over a set period, usually an academic year. Generally, to qualify for a high school diploma, a certain number of academic credits needed must be accumulated. The requirements can differ significantly by state. Understanding these variances is vital to ensure students meet the necessary graduation prerequisites.
Required Courses for Graduation
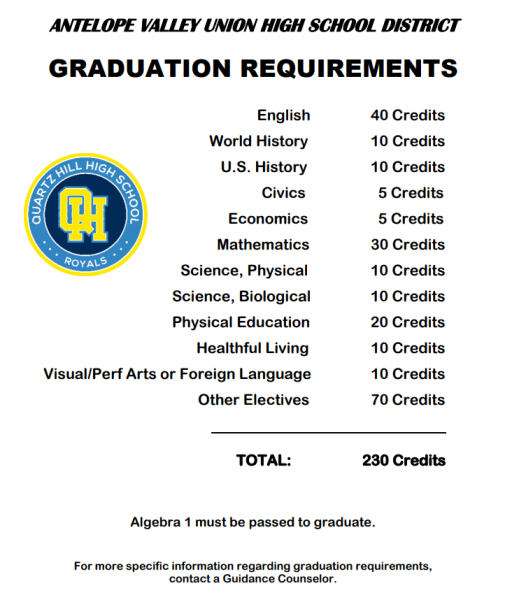
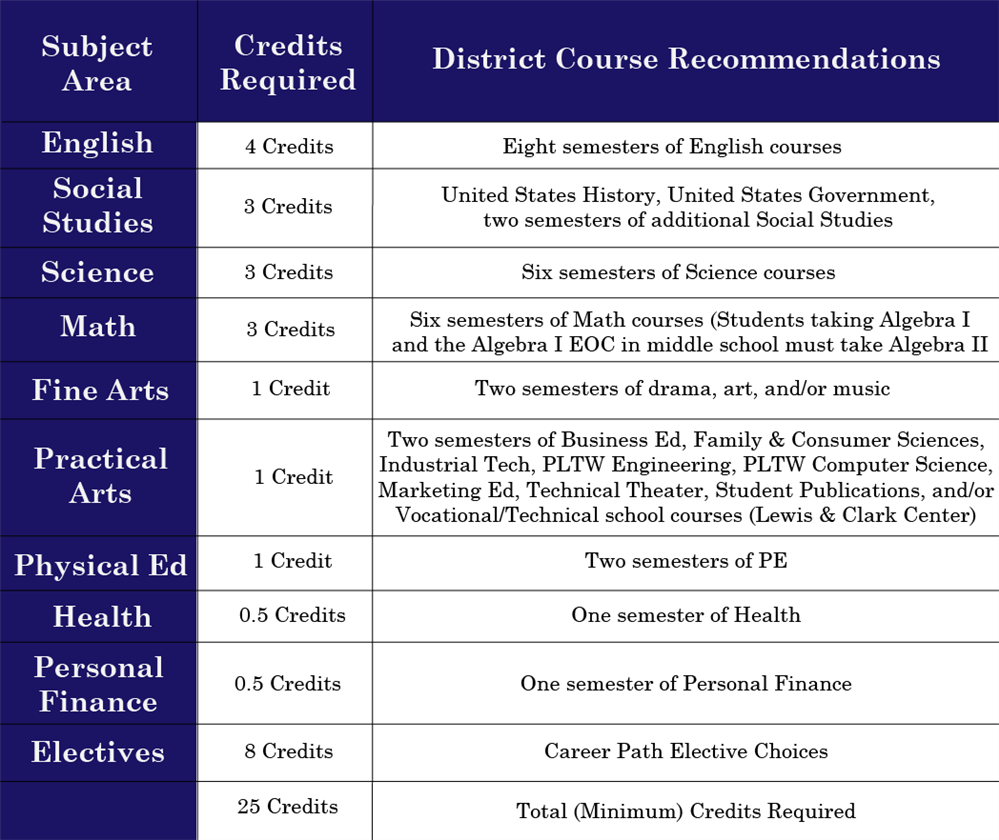
Typically, most states require students to complete a combination of core courses and electives. The core course requirements usually include subjects such as English language arts, mathematics, science, and social studies. For instance, the standard may require 4 credits in English, 3 in math, and 3 in science, among others. Each state will specify the credits for high school diploma needed in these areas and might include specific benchmarks. It’s crucial to regularly assess and ensure that these requirements are being satisfied across the high school career.
Tracking High School Credits
Effective tracking of graduation credit total is essential for students aiming to meet their high school graduation standards. Schools typically provide students with a credit evaluation mechanism through report cards or progress monitoring systems. By maintaining updated records of completed and in-progress courses, students can avoid last-minute surprises regarding their standing. Parents and guardians also play a crucial role in checking credit completion, helping monitor the academic progress.
Elective Credits Needed
In addition to core subjects, students often have options for elective courses. These elective credits needed allow students to explore personal interests or focus on vocational training. It is important to note that fulfilling elective requirements not only contributes to the overall credit total but also enriches the high school experience, potentially influencing future education or career choices.
Credit Distribution for Graduation
The credits breakdown for diploma typically involves a mix of required core courses and electives. Most states recommend around 22 to 26 total credits for graduation. For instance, a sample distribution might involve 4 credits in English, 3 in math, 3 in science, 3 in history, alongside 2-4 elective credits depending on the state’s specific policies. This organized approach provides students a roadmap to fulfill their education requirements to graduate.
Steps to Meet Credit Requirements
One of the effective strategies for students to stay on track is mapping out their courses early. Utilizing a planner to track how to earn high school credits, including summer courses or online programs, can be beneficial. Additionally, dual enrollment programs allow students to earn both high school and college credits, facilitating a faster track toward graduation while also introducing students to higher education.
Challenges in Earning High School Credits
Various factors contribute to challenges in accumulating necessary credits. For instance, attendance policies can influence credit earning as prolonged absences often lead to falling behind. Understanding these high school policies on credits and any associated remedial programs is crucial in achieving academic success. Schools often provide support services to help students navigate these issues, and proactive engagement with guidance counseling can facilitate appropriate adjustments in course loads for balance.
The Importance of High School Graduation Standards
High school graduation can significantly impact a student’s future academic and career opportunities. Maintaining certain academic achievement metrics and adhering to the high school graduation standards helps ensure students are well-equipped for post-educational life. Knowledge of total credits for high school dictates strategic planning for future academic engagements and commitments.
Future Implications of Credit Accumulation
Completing the necessary credits for high school diploma is not just about meeting state requirements; it’s about building a foundation for future success. Employers, and higher education institutions, often examine transcripts closely, looking at not just the total credits but also the grades achieved. Therefore, good study habits, attendance, and a proactive approach to education play vital roles in effective credit accumulation.
Parental Engagement in Education Pathways
Research shows that parental involvement greatly enhances student success. Parents should cultivate an active role in tracking academic progress, keeping open lines of communication with teachers, and attending school meetings. Such engagement empowers students to meet their graduation goals while fostering a supportive learning environment. Guidance counselors also play a crucial role in this process, aiding families in understanding the graduation criteria unique to their state.
Key Takeaways
- Students typically need between 22 to 26 credits to graduate high school, depending on state requirements.
- Core courses notably include English, math, science, and social studies, supplemented with required electives.
- Managing and tracking credits should involve both students and parents, leveraging school resources for guidance.
- Engagement and involvement play significant roles in student success, influencing credit completion and achievement.
- Future educational and career paths can be shaped by how well students manage their high school credits.
FAQ
1. What factors influence credit accumulation in high school?
Several factors influence students’ ability to accumulate necessary high school credits. Attendance is critical, as prolonged absences can lead to significant credit loss. Student engagement, along with their ability to maintain effective study habits, also significantly affects credit accrual. Parental support and interaction with faculty further enhance students’ likelihood of meeting graduation prerequisites.
2. How many electives must students complete for graduation?
The number of electives required can vary by state, but typically students are expected to complete 2 to 4 elective credits. Engaging in elective courses provides students a chance to explore diverse subjects, equipping them with skills relevant to future studies or occupations. It’s advisable for students to verify with their academic counselors regarding specific requirements.
3. Can summer school help in credit recovery?
Yes, summer school offers credit recovery options for students who may not have completed required courses during the regular academic year. Many schools provide summer programs allowing students to focus on the subjects or credits they need to stay on track for graduation.
4. What alternative pathways exist for earning high school credits?
Students have a variety of pathways available for earning high school credits, including online courses, community classes, and dual enrollment in college courses. Engaging in independent study or projects may also satisfy certain credit requirements, depending on school policies.
5. How do I check my credit completion status?
Students can typically check their credit completion status by reviewing their academic records with school counselors. Many schools also provide online portals where students can track their credit accumulation, updates regarding grades, and completed courses, helping to ensure they stay aligned with graduation requirements.