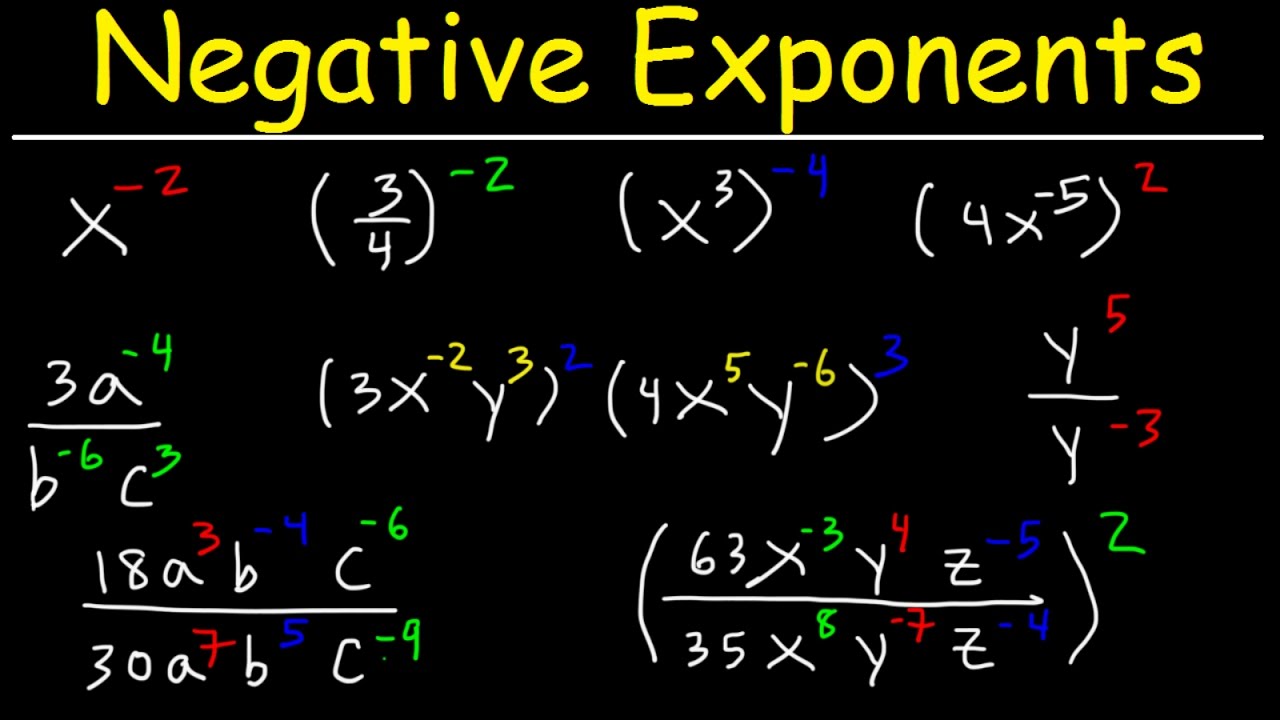Smart Ways to Master Negative Exponents: Achieve Clarity in 2025!
Understanding Negative Exponent Rules
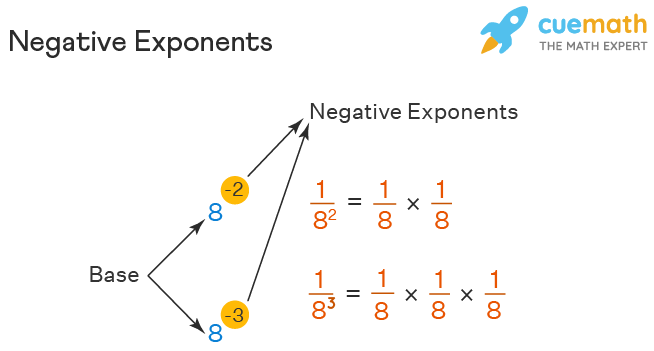
To master negative exponent rules, one must first understand that a negative exponent indicates a reciprocal. In mathematical notation, for any non-zero base number \( a \) and positive integer \( n \), the rule can be defined as:
\[
a^{-n} = \frac{1}{a^n}
\]
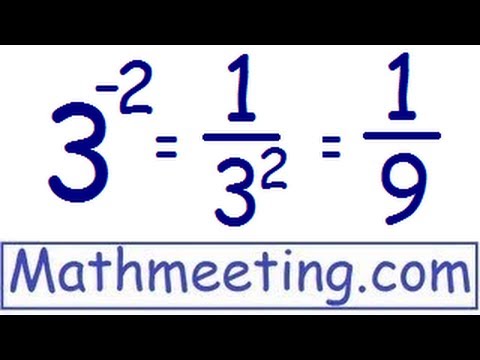
This essential rule simplifies the process of simplifying negative exponents in various mathematical operations. For example, \( 2^{-3} \) can be expressed as \( \frac{1}{2^3} \) or \( \frac{1}{8} \). By grasping these foundational concepts, learners can approach more complex applications with confidence and clarity. Understanding how to manipulate negative exponents enhances problem-solving skills and mathematics fluency.
Negative Exponent Meanings: More Than Just the Sign
The negative exponent meanings can be better grasped through practical examples. The transformation of a negative exponent into a positive one is a key concept. For instance, \( x^{-2} \) translates to \( \frac{1}{x^2} \), while \( (3y)^{-1} \) becomes \( \frac{1}{3y} \). Understanding this principle is imperative for solving algebraic equations effectively. This knowledge facilitates work in advanced topics such as rational functions and exponential growth, providing a solid foundation in mathematical principles.
Using Negative Exponents in Real-Life Applications
Moreover, the negative exponent application extends to various fields, including physics and economics, where formulas often involve reciprocals. For example, in calculating gravitational force, the equation includes terms with negative exponents, emphasizing inverse relationships. A strong grasp of negative exponent calculations prepares students not only for academic challenges but also for real-world scenarios. Engaging with real-life examples fosters a deeper understanding and encourages practical usage of mathematical concepts.
Simplifying Negative Exponents with Ease
Simplifying negative exponents involves various methods that can be strategically implemented. The application of exponent laws plays a crucial role in resolving complex expressions featuring negative exponents. One effective approach is to combine like base numbers. For instance, when simplifying expressions like \( a^{-n} \cdot a^{m} \), the result follows the law:
\[
a^{-n} \cdot a^{m} = a^{m-n}
\]
This law shows how to manage negative exponent fractions seamlessly during operations. Ensuring familiarity with these rules helps students simplify expressions efficiently while minimizing potential pitfalls in their calculations.
Step-by-Step Guide to Converting Negative Exponents
Converting negative exponents can initially be challenging, but a systematic guide provides clarity. Start with identifying the base number and its exponent. For example, in the expression \( (5^{-2})^{-3} \):
1. Recognize what the negative exponent signifies—take the reciprocal.
2. Rewrite it as \( 5^{-2} = \frac{1}{5^2} \).
3. Raising that expression to another negative exponent involves finding its positive counterpart.
4. Thus, \( (5^{-2})^{-3} = (5^2)^3 = 5^{6} = 15625 \).
This step-by-step approach unpacks simplifying negative exponents methods and aids in grasping complex applications.
Negative Exponents in Equations: Examples and Strategies
Incorporating negative exponent equations within mathematical problems can enrich problem-solving experiences. For example, an equation like \( 3x^{-1} + 2 = 7 \) becomes easier when translated. First, rewrite it as:
\[
3 \cdot \frac{1}{x} + 2 = 7
\]
Solving for \( x \) involves isolating the variable:
1. Subtract 2 from both sides: \( 3 \cdot \frac{1}{x} = 5 \).
2. Multiply by \( x \) to find \( x\): \( 3 = 5x \Rightarrow x = \frac{3}{5} \).
Using negative exponent properties to transform equations helps build mathematical confidence and improve leisure in learning mathematics.
Challenges and Common Mistakes with Negative Exponents
Learning about negative exponent concepts involves overcoming common challenges that many learners face. One frequent pitfall includes misunderstanding the reciprocal property, specifically confusing \( a^{-n} \) with \( -a^n \). To avoid such errors, educators and students can emphasize consistent practice using negative exponent worksheets and negative exponent quizzes designed to reinforce understanding. Furthermore, collaborative group studies can enhance engagement and foster healthy practice routines.
Graphing Negative Exponents: Visualization Techniques
Graphing functions that involve negative exponents can create meaningful discussions in terms of exponential decay. For example, the function \( y = x^{-1} \) results in a hyperbola asymptotic to the x and y-axes. By plotting this function using graphing techniques, students can visualize their learning effectively, making concepts stick. Utilizing tools that integrate graphing and calculations helps clarify the concept of inverse relationships associated with negative exponent operations.
Negative Exponent Exercises: After-learning Engagement
To solidify understanding further, consistent engagement through negative exponent exercises and real life applications provides unique insights. Suggestions like interacting with fractional expressions or experimenting with mathematical notation challenge learners. Implementing such exercises facilitates retention and allows students to embark on the practice of applying negative exponents efficiently. This varied exposure promotes adaptable skills in mathematics and critical thinking.
Future Directions: Enhancing Understanding with Resources
As we approach a new era of mathematical education, the emphasis on understanding negative exponent properties is vital. Comprehensive resources portend a future brimming with potential for improved comprehension in math logistics. Utilizing educational resources such as online videos, interactive software, and tutoring sessions fosters increased engagement and assists learners in grasping complex math fundamentals. Personalized learning systems adapt to each student’s pacing, ensuring that math lessons regarding exponents are dynamic and understanding is further improved.
Teaching Strategies for Negative Exponents
Effective educational strategies in teaching negative exponents can greatly enhance clarity among students. Utilizing visual aids and hands-on activities where learners manipulate numbers and expressions in real-time helps them develop intuitive grasp over teaching negative exponents. This establishes a solid educational approach that integrates technology while keeping students engaged. Moreover, leveraging interactive tools can facilitate an understanding of negative exponent growth, enhancing student comprehension through practical exposure.
Engagement through Negative Exponent Quizzes
Regularly implementing negative exponent quizzes promotes a culture of continual learning. These quizzes can help students gauge their grasp of the concepts while offering opportunities for immediate feedback. By providing varying difficulty levels in problem sets, educators might tailor learning experiences to different proficiency levels. Collectively, this is beneficial for individual student understanding and builds a supportive learning environment focused on growth and mastery.
Key Takeaways
- Mastering negative exponent rules transforms the understanding of mathematical operations.
- Negative exponents indicate the reciprocal of the base number raised to the positive exponent.
- Applying these concepts in real-life situations enriches learning and retention.
- Collaborative engagement enhances learning experiences while overcoming challenges.
- Utilizing diverse educational resources can significantly improve mathematical comprehension.
FAQ
1. What are the main rules for simplifying negative exponents?
When simplifying negative exponents, the foundational rule is recognizing that \( a^{-n} = \frac{1}{a^n} \). Using this, you can convert negatives into positives for easier calculations. It helps maintain the flow of arithmetic operations and promotes a solid grasp over exponent properties.
2. Why is it important to learn about negative exponent properties?
Understanding negative exponent properties is crucial because it forms a base for higher mathematical concepts and prepares students for algebraic operations often necessary in scientific fields. The clarity it brings in reciprocal relationships greatly enriches comprehension in both academic and practical contexts.
3. How can negative exponent examples help in mastering the subject?
By working through negative exponent examples, students experience hands-on learning that reinforces concepts. Practical application allows them to develop problem-solving strategies effectively, fostering adaptable skills necessary for tackling complex mathematical relationships.
4. What are some effective strategies for teaching negative exponents?
Effective strategies for teaching negative exponents include using visual aids, interactive activities, and collaborative learning environments. These engagements help students to better grasp the reciprocal nature of negative exponents, making complex abstract concepts more tangible through experiences.
5. Where can I find additional resources for negative exponent practice?
Numerous educational platforms provide supplementary resources and exercises for mastering negative exponents, including worksheets, quizzes, and targeted feedback. Websites dedicated to mathematics education often feature extensive materials tailored to various learning levels, enhancing overall understanding.
6. Can negative exponents be involved in graphing equations?
Yes, negative exponents can be integral to graphing equations. Functions like \( y = x^{-2} \) demonstrate classic exponential decay, where the resulting graphs showcase unique behaviors like approaching the x-axis again. This visualization helps students comprehend inverse relationships effectively.
7. How can negative exponents provide clarity in math fundamentals?
Negative exponents elucidate mathematical operations by indicating the importance of reciprocals in computations. Validating their properties reinforces foundational concepts in mathematics, thereby improving overall understanding and competence in higher mathematical pursuits.