Understanding Negative Exponents: Simplifying Math in 2025
Grasping the Concept of Negative Exponents
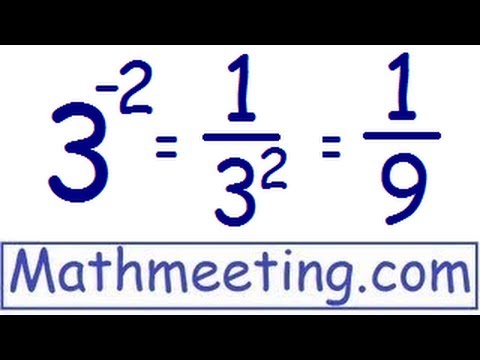
Negative exponents can initially seem daunting, but by breaking down their definitions and applications, learners can easily start mastering this fundamental aspect of **exponentiation**. A **negative exponent** indicates the reciprocal of the base raised to the opposite positive exponent; for instance, x-n equals 1/xn. Understanding this concept lays the groundwork for many mathematical fields, such as algebra and calculus. With a solid grasp of **negative exponent rules**, students are better equipped to tackle equations involving **fractional bases** and ultimately, build their comprehension of more complex **mathematical concepts**.
Negative Exponent Definition and Applications
The **definition of negative exponents** can be articulated as the expression that represents the inverse of a number, serving as a vital feature of **algebraic expressions**. For example, if we encounter the expression 2-3, it can be rewritten as 1/23. This transformation is particularly useful in real-world applications, such as in physics where **exponentiation** describes phenomena like **exponential decay**. Recognizing the correlation between **negative numbers** and **negative exponent operations** facilitates the learning process by grounding it in real-life contexts.
Examples of Negative Exponents in Mathematics
To further clarify the idea of **negative exponent operations**, let’s consider some examples. For instance, if we take 5-2, applying the negative exponent rule results in 1/52 = 1/25. This helps illustrate how raising to negative powers effectively shifts values to a **denominator**. Such transformations extend beyond numeric calculations, playing critical roles in **dividing exponents** and converting **fraction powers** in **exponential functions**. Adding layers of complexity, one can uncover how **roots of numbers** are intrinsically linked with negative exponents, enriching the way we visualize and teach **exponentiation**.
The Laws of Exponents Simplified
The **laws of exponents** provide a systematic approach to manipulating expressions involving bases and exponents. These essential principles act as guidelines for simplification, making them practical tools in algebra. Consistently using these **exponent rules**, such as the Power of a Power Rule or the Product Rule, helps students simplify expressions effectively. For example, when multiplying two expressions with the same base, as in am \* an, one simply adds the exponents: am+n. Understanding and applying these crucial rules allows students to approach **equations with exponents** with confidence.
Multiplying and Dividing Exponents: Key Insights
Multiplication and division of exponents hinge upon established rules that simplify the process. When **multiplying exponents**, remember to apply the base consistently and add the exponents. In contrast, for **dividing exponents**, it is crucial to subtract the exponents under the same base, as in the equation am/an = am-n. Grasping these laws is essential for **simplifying expressions**, making them foundational for future mathematical endeavors. Moreover, when teaching this part of exponents, providing visual aids can significantly assist in comprehension and retention—helping learners see the relationship between **exponentiation** and its algebraic manifestations.
Inverse Operations: Understanding Reversal through Negative Exponents
The relationship between **negative exponents** and **inverse operations** fosters a deeper understanding of both concepts. In instances such as x-a = 1/xa, it becomes clear that **negative exponent implications** serve to demonstrate this relationship further. Students frequently develop a misunderstanding of how negative exponents are utilized. Therefore, being aware of **common mistakes with exponents** and frequently reinforcing the associative roles played by these rules can enhance students’ understanding of powers and roots. Real-world examples can also be helpful, such as explaining how **fractional exponents** often depict rates in fields like finance or science.
Simplifying Expressions: Practical Steps
When faced with complex expressions that involve both positive and **negative exponents**, simplifying them requires a systematic approach. Begin by applying the various exponent rules methodically, ensuring the bases are uniform wherever possible. Next, keep an eye on terms with **fraction powers** and restructure them into standard form to unveil underlying patterns. Instruction that incorporates clear, logical steps ensures that the students understand how to efficiently manipulate radical expressions. By doing so, learners can more easily arrive at solutions without becoming overwhelmed.
Practical Example: Transforming Expressions
To illustrate how to break down and simplify a complex expression, let’s analyze (2-3 * 42) / (8-1 * 160.5). By applying the rules step-by-step, we realize that 2-3 becomes 1/23, while 160.5 is simplified to 4. Rewriting the entire expression will leave us manipulating numbers and exponents more readily. This demonstration exhibits how to effectively handle **exponential functions** while simultaneously reinforcing the underlying principles governing exponent relationships.
Advanced Techniques for Handling Exponents
Advanced mathematical concepts, including **scientific notation**, utilize negative exponent frameworks extensively. Such applications are particularly advantageous in scenarios where numerals must be represented compactly. Additionally, students should learn how **exponential functions** function mathematically and how these graphs depict growth or decay. Heightening their understanding requires educators to incorporate technology and interactive learning tools into their teaching methods. Providing readily accessible educational resources, such as worksheets or online tutorials focusing on the **converting of exponent forms**, will allow students to practice and grasp fundamentals more effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding **negative exponents** is fundamental for simplification and clarity in mathematics.
- The **laws of exponents** guide students in systematically solving equations involving various bases.
- Knowledge of **negative exponent properties** underpins many aspects of real-world applications, including scientific notation.
- Utilizing practical examples enriches understanding, especially in transforming and simplifying expressions.
- Applying advanced techniques enhances comprehension and introduces students to broader algebraic concepts.
FAQ
1. What are some common misconceptions about negative exponents?
A prevalent misconception is that **negative exponents** denote negative values. In reality, they indicate that the base represents a fraction; understanding this perspective is crucial to clear up confusion and allows students to recognize connections between powers and their manipulations.
2. How do negative exponent rules vary from standard exponent rules?
Many **negative exponent rules** are grounded in similar principles as standard **exponent rules**, yet they emphasize the reciprocal nature of negative powers by introducing new contexts for simplification. Familiarity with these alternative perspectives creates a robust framework for dealing with algebraic expressions more effectively.
3. Can you provide examples of negative exponents in real life?
In fields like physics or finance, negative exponents frequently appear in formulas for calculating decay rates, discount factors, or scientific measures. These instances illustrate how **exponentiation** functions crucially address practical problems involving various bases and powers.
4. What strategies help with understanding negative exponents?
Using visual aids, engaging with practical examples, and systematic practice through worksheets can significantly bolster students’ understanding of **negative exponent definitions**. Enabling students to experience exponents’ interconnected nature across contexts enhances their learning experience.
5. Are there educational resources available for learning negative exponents?
Yes, numerous resources exist online, including **mathematics worksheets**, study guides, and instructional videos, all catering to students looking to improve their grasp on **exponentiation** concepts. Utilizing these resources can bridge gaps in understanding and facilitate further learning.
6. How do properties of powers assist in simplifying exponent expressions?
The **properties of powers** stem from the fundamental **exponent rules** and simplify expressions involving multiplication and division of like bases more efficiently. Understanding these properties empowers students to recognize patterns and allows them to manipulate complex equations with confidence.
7. What role does technology play in teaching exponents?
Innovative technologies, such as interactive math platforms and educational videos, make learning about exponents engaging and effective. Educators can integrate these methods into their lesson plans to enhance students’ comprehension of **negative exponent operations** while encouraging collaboration and exploration within mathematical frameworks.